



6a.2. Applications
There are many "applications" we could discuss. Here we focus on some of the most popular communications mechanisms (media) of the Internet for historical purposes and to help categorize, or perhaps generalize, some specific apps.
Before delving into user-user communications applications, we will skim over a few that do not easily fit that category. Then define a few general categories we can use to group apps. Followed by a, sometime historical, look at key apps. We end this section by skimming over some of the most popular mobile apps.
- search engines
- Seach engines allow us to find stuff. They will be the focus of the module on Internet reseach.
- application distribution
- Most apps are now purchased, downloaded and installed from the Internet. In the desktop/laptop arena, this is still done mostly (safely) from a web site owned by the software creator, for example, getting PDF Reader directly from Adobe. In the mobile world, there is often one or more distinguished (safe) sites for app download, such as Google Play and Apple's App Store (iTunes). (In the sense used here, there are many "distinguished sites for the desktop world - Google it before using it.)
- mapping software
- It seems most people couldn't find their way to the local market without using mapping software to plan the route and direct them. The best include traffic updates, automatic rerouting, and overhead views. At least one, Waze, combines social interaction with mapping.
- e-commerce
- We buy a lot using the Internet and there is a plethora of apps that try to make it easy, secure, cheaper, etc. It should be clear why there is a great deal of competition in this area. That it is a "thing", is made clear by Black Friday Of key importance to me is that you understand when you should be using a secure system – some, like online banking services, are proprietary, but when using the web look for HTTPS. The "S" indicates a certain minimal amount of security you should expect for such transactions (or personal information or passwords).
- weather
- It seems impossible to live without continuous updates on the weather. All of these start with information produced (on supercomputers) at the National Weather Service and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. They are distinguished primarily by what they add (their own meteorologists, graphics, etc.) and their user interfaces. Alerts are important to many people.
- cloud file storage
- Many of us are using the benefits provided by online backups, synchronization across devices, and file sharing provided by cloud services. Your primary concern here should be security – think of it like original documents placed in a safety deposit box. How secure is your service?
Communications Apps
You may find that you believe some of the apps that follow belong above. For example, streaming videos from Netflix may be less "communication" than using mapping software that can tell you about local points of interest or deals. It is perhaps a distinction in my mind only, but in this case I was thinking of apps like Facebook livestream. It gets complicated – Netflix allows you to share what you have watched – and beg your indulgence.
e-mail [src]
Electronic mail, commonly called email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients using the Internet. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver and store messages. Neither the end users nor their computers are required to be online simultaneously; they need connect only briefly, typically to an email server, for as long as it takes to send or receive messages.
An email message consists of three components: the message envelope, the message header, and the message body. The message header contains control information, minimally including an originator's email address and one or more recipient addresses. Usually descriptive information is also added, such as a subject header field and a message submission date/time stamp.
Originally a text-only (7-bit ASCII) communications medium, email was extended to carry multi-media content attachments, like a picture, that have come to be called Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME). A MIME extension, or attachment, may be just about anything, a picture, an audio file, or even a program – however there are limits to how much can be attached, and to your mailbox size.
Electronic mail predates the inception of the Internet, and played a crucial role in creating it. The history of modern, global Internet email services reaches back to the early ARPANET. Standards for encoding email messages were proposed as early as 1973. Conversion from ARPANET to the Internet in the early 1980s produced the core of the current services. An email sent in the early 1970s looks quite similar to a basic text message sent on the Internet today.
Network-based email uses the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
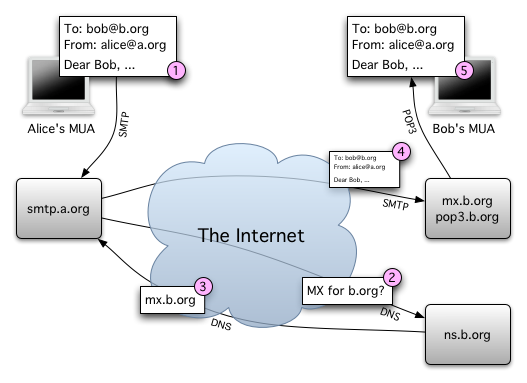
How e-mail works, includes looking up "mail exchange" (MX) information for the receiving host
By Gdr (Uploaded by author to English Wikipedia) [GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons
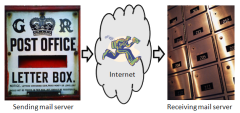
Email Delivery. (Email can wait at either end.)
By Paul Mullins: Constructed with public domain image
webmail
Traditional email was sent from the source to a destination host that saved it for the recipient. Users accessed the email using an application on that host. It could only be accessed from a different computer by remotely connecting to the mail server first. Some email clients, like Outlook, make this connection for you, typically using the POP3 protocol.
Web-based email or webmail is accessed through the web and stays on the web (something like cloud computing). The main benefit is that the user can access their mail from any location with any computer that has an Internet connection and a web browser.[src]
 #180 Outlook begone! Use Gmail
#180 Outlook begone! Use Gmail
ATmail interface
Uploaded by Atmail. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
XPN Newsreader ScreenShot

"Big 8 + alt: Top level of subject hierarchies (For example: alt.binaries.games.xbox360)
Benjamin D. Esham / Wikimedia Commons [CC-BY-SA-2.5], via Wikimedia Commons
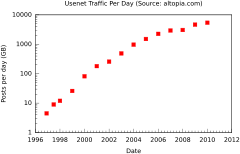
Average amount of Usenet traffic per day
public domain image
Newsgroups [src]
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from many users in different locations, and open to anyone. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read newsgroups.
Despite the advent of file-sharing technologies such as BitTorrent, as well as the increased use of blogs, formal discussion forums, and social networking sites, coupled with a growing number of service providers blocking access to Usenet, newsgroups continue to be widely used. In fact, usage is still growing!
Typically, a newsgroup is focused on a particular topic of interest. Some newsgroups allow the posting of messages on a wide variety of themes, regarding anything a member chooses to discuss as on-topic, while others keep more strictly to their particular subject, frowning on off-topic postings. The major set of worldwide newsgroups is contained within nine hierarchies, eight of which are operated under consensual guidelines that govern their administration and naming. The current Big Eight are shown at left.[src]
The news admin (the administrator of a news server) decides how long articles are kept on her server before being expired (deleted). Different servers will have different retention times for the same newsgroup; some may keep articles for as little as one or two weeks, others may hold them for many months. Some admins keep articles in local or technical newsgroups around longer than articles in other newsgroups.

Despite the ephemeral sound this gives newsgroup postings, much of the content was (and is) saved. Assume that anything you put on the Internet is there to stay. The sidebar is a "must read".
Discussion groups relate to many current forms of communication, especially Internet Forums.
Discussion boards [src]
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are at least temporarily archived. Also, depending on the access level of a user and/or the forum set-up, a posted message might need to be approved by a moderator before it becomes visible.
Forums have a specific set of jargon associated with them; e.g. A single conversation is called a "thread". (Many mail readers now display message in threads.)
A forum is hierarchical (tree-like) in structure: a forum can contain a number of subforums, each of which may have several topics. Within a forum's topic, each new discussion started is called a thread, and can be replied to by as many people as wish to.
Depending on the forum set-up, users can be anonymous or have to register with the forum and then subsequently log in in order to post messages. Usually, users do not have to log in to read existing messages.
The modern forum is similar to (Usenet) newsgroups, and are a technological evolution of the dialup bulletin board system. Newsgroups are characterized by less central control, rarely having moderated groups, and generally allowing anyone to post (anonymously).
The discussion boards on most course management services, like D2L – used at SRU – are essentially organized as described here.

The phpBB Internet Forum software package, one of the most popular forum packages.
By Meow (Own work) [GPL], via Wikimedia Commons

Screenshot of the FUDforum software
By Own work (FUDforum's website) [GPL], via Wikimedia Commons
Blog [src]
A blog (a blend of the term web log) is a type of web site or part of a web site. Blogs are usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video. Entries are commonly displayed in reverse-chronological order. Blog can also be used as a verb, meaning to maintain or add content to a blog.
Most blogs reflect the thoughts, opinions, and biases of the individual or corporation that runs the blog. However, most are also interactive, allowing visitors to leave comments and even message each other via widgets on the blogs. This interactivity distinguishes them from other static web sites.
Many blogs provide commentary or news on a particular subject; others function as more personal online diaries. A typical blog combines text, images, and links to other blogs, web pages, and other media related to its topic. Most blogs are primarily textual, although some focus on art (art blog), photographs (photoblog), videos (video blogging), music (MP3 blog), and audio (podcasting). Microblogging is another type of blogging, featuring very short posts. Examples of microblogging are Twitter and FaceBook status updates.
Blogs are still widely used. If you extend the idea of a blog post to a YouTube video, or even a product description on Amazon, along with the comments that follow, you can see that this model is very wide-spread indeed.
SG screenshot of Foundation blog
public domain image

choqoK, the KDE micro-blogging client
By Mtux (Own work) [GFDL, CC-BY-SA-3.0 or FAL], via Wikimedia Commons
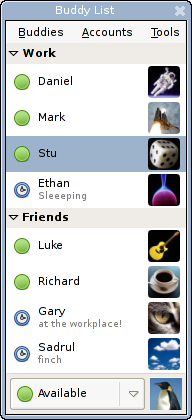
Pidgin 2.0 contact window
By Pidgin team (http://pidgin.im/pidgin/about/) [GPL], via Wikimedia Commons
Unix Talk command, circa 1990
Uploaded by Porao. Licensed under GNU General Public License
IM [src]
Instant messaging (IM) is a form of real-time direct text-based communication between two or more people using personal computers or other devices, along with shared clients. The user's text is conveyed over a network, such as the Internet. More advanced instant messaging software clients also allow enhanced modes of communication, such as live voice or video calling.
IM falls under the umbrella term online chat, as it is a real-time text-based networked communication system, but is distinct in that it is based on clients that facilitate connections between specified known users (often using "Buddy List", "Friend List" or "Contact List"), whereas online 'chat' also includes web-based applications that allow communication between (often anonymous) users in a multi-user environment.
Online chat and instant messaging differs from other technologies such as e-mail due to the perceived synchronicity of the communications by the users –chat happens in real-time. Some systems permit messages to be sent to people not currently 'logged on' (offline messages), thus removing some of the differences between IM and e-mail (often done by sending the message to the associated e-mail account).
IM allows effective and efficient communication, allowing immediate receipt of acknowledgment or reply. In many cases instant messaging includes additional features which can make it even more popular. For example, users can see each other by using webcams, or talk directly for free over the Internet using a microphone and headphones or loudspeakers. Many client programs allow file transfers as well, although they are typically limited in the permissible file-size.
It is typically possible to save a text conversation for later reference. Instant messages are often logged in a local message history, making it similar to the persistent nature of e-mails.
A key difference between modern IM and its ancestors is that the user is informed when a "buddy" or "contact" becomes available.
There are many modern apps that support text-based communication. Facebook Messenger certainly qualifies in this regard. Even "texting" (SMS/MMS) is a relative of this kind of technology.
Author of the tweet: Klaus Graf, citing text from an anonymous Swabian text collection from the 15th century.
public domain image follows twitter guidelines
XChat, a cross-platform IRC client.
By Original unloader was Moniker42 at en.wikipedia [GPL], via Wikimedia Commons
twitter [src]
Twitter is a social networking and microblogging service, enabling its users to send and read messages called tweets. Originally, tweets were simply text-based posts of up to 140 characters displayed on the user's profile page. Twitter was compared to a web-based Internet Relay Chat (IRC) client.
Today, Twitter serves as an important source of news, and allows both photos and videos.
Tweets are publicly visible by default; however, senders can restrict message delivery to just their followers. Users can tweet via the Twitter website, compatible external applications (such as for smartphones), or by Short Message Service (SMS) used to send text messages on phones.
Users may subscribe to other users' tweets – this is known as following and subscribers are known as followers or tweeps (Twitter + peeps).
Twitter allows users the ability to update their profile by using their mobile phone either by text messaging or by apps released for certain smartphones & tablets.
 Twitter 2016: A Tough Year In Review |
 Twitter Releases 2016 Trending Topics |
 I tried Twitter back when it was a new thing. I decided no one would really want to follow my ramblings, but followed some handful of "institutions" that I cared about, for example NASA. I found that every one of them felt the need to tweet at least daily, even when they had nothing to say... I dumped it. In Dec, 2016 I reinstalled, because it seems that my new President will communicate with the people that way.
I tried Twitter back when it was a new thing. I decided no one would really want to follow my ramblings, but followed some handful of "institutions" that I cared about, for example NASA. I found that every one of them felt the need to tweet at least daily, even when they had nothing to say... I dumped it. In Dec, 2016 I reinstalled, because it seems that my new President will communicate with the people that way.Their user-base should be soaring.
Facebook [src]
Facebook is a social networking service and web site. Facebook has more than 1.65 billion monthly active users as of March 31, 2016. [See the list of virtual communities with more than 100 million active users.]
Users may create a personal profile, add other users as friends, and exchange messages and post status updates, with automatic notifications. Facebook posts include photos, videos, and live streaming. Additionally, users may follow a business or join common-interest user groups, organized by workplace, school or college, or created by an individual.
Facebook users must register before using the site. Facebook allows any users who declare themselves to be at least 13 years old to become registered users of the web site. The name of the service stems from the colloquial name for the book given to students at the start of the academic year by university administrations in the United States to help students get to know each other better.
A January 2009 Compete.com study ranked Facebook as the most used social networking service by worldwide monthly active users, followed by MySpace. (Isn't history neat?) Facebook still ranks as the largest virtual community including 78% of the US population.
Sidebar on social networks and social change
VoIP
Voice Over Internet Protocol is a type of internet telephony in which the Internet is used to make phone calls or send messages, either one on one or for audio-conferencing. You can make long distance phone calls that are surprisingly cheap or even free.[src]
Skype is one of the most popular programs that provides voice over Internet (using a proprietary protocol). Skype is a peer-to-peer software application that allows users to make voice and video calls and chats over the Internet. Calls to other users within the Skype service are free, while calls to both traditional land line telephones and mobile phones can be made for a fee using a debit-based user account system. However, due to Skype being partially free, it is illegal in some countries. Skype has also become popular for its additional features which include instant messaging, file transfer, and video conferencing.[src]
Converting (analog) voice signals to digital for transmission through the network, and then back to analog, is accomplished by a codec. (Codecs are used for podcasting, webcasting, and YouTube videos also.)
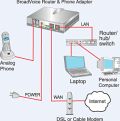
Home phone using VoIP
Uploaded by JMPerez. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 1.0 Generic license.

Mac Skype
By Skype INC, Jeremy Zhang (Skype) [see page for license], via Wikimedia Commons

Typical Webcast
By Spark Street Digital LLC (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
webcast [src]
A webcast is a media file distributed over the Internet using streaming media technology to distribute a single content source to many simultaneous listeners/viewers. A webcast may either be distributed live or on demand. Essentially, webcasting is "broadcasting" over the Internet.
The largest "webcasters" include existing radio and TV stations, who "simulcast" their output, as well as a multitude of Internet only "stations". The term webcasting usually refers to non-interactive linear streams or events. Rights and licensing bodies offer specific "webcasting licenses" to those wishing to carry out Internet broadcasting using copyrighted material.
podcast [src]
A podcast (or non-streamed webcast) is a series of digital media files (either audio or video) that are released episodically and often downloaded through web syndication. The word replaced webcast in common use with the success of the iPod and its role in the rising popularity and innovation of web feeds.
The mode of delivery differentiates podcasting from other means of accessing media files over the Internet, such as direct download, or streamed webcasting. A list of all the audio or video files currently associated with a given series is maintained centrally on the distributor's server as a web feed, and the listener or viewer employs special client application software known as a podcatcher that can access this web feed, check it for updates, and download any new files in the series. This process can be automated so that new files are downloaded automatically. Files are stored locally on the user's computer or other device ready for offline use, giving simple and convenient access to episodic content.

Mozilla Firefox RSS feed icon
By unnamed (Mozilla Foundation) (feedicons.com, siehe unten) [GPL or LGPL], via Wikimedia Commons

Podcast Picture of the radio show "The Buzz" – public domain image
youtube [src]
YouTube is a video-sharing website on which users can upload, share and view videos. YouTube uses multiple technologies (formats) to display a wide variety of user-generated video content, including movie clips, TV clips, and music videos, as well as amateur content such as video blogging and short original videos. Most of the content on YouTube has been uploaded by individuals, although media corporations including CBS, BBC, Vevo, Hulu, and other organizations offer some of their material via the site, as part of the YouTube partnership program.
Unregistered users may watch videos, and registered users may upload an unlimited number of videos. Videos that are considered to contain potentially offensive content are available only to registered users 18 years old and older.
wiki [src]
A wiki is a web site that allows the creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language, or a WYSIWYG text editor. Wikis are typically powered by wiki software and are often used collaboratively by multiple users. Examples include community web sites, corporate intranets, knowledge management systems, and note services. The software can also be used for personal note taking.
Most-Used Mobile Apps
Many of the most-used apps belong to one of the generic categories already discussed. They are collected here for comparison to (the usage of) other apps. The list: These are the 25 most popular mobile apps in America was published by Quartz. It is based on the number of unique (18+ years old) users for the app, with the number in millions.
You should note how dominant Facebook & Google are (they each own multiple apps), that there are no games, and that the only subscription-based service is Netflix.
While you have probably heard of all of these apps, take a moment to explore one or more that you do not actively use. For the class, you want a general sense of which apps are used the most and what they do, while keeping in mind that the vast majority of apps are not even on this list. The Android app marketplace is the wild, wild, west compared to Apple and, as of June 2016, there were over 2 million Apple apps to choose from.
You will find that the quality of linked YouTube videos varies dramatically. I apologize for poor production quality, expletives, strange pop-ups and the other things people of the e-generation have grown used to. You might also note that many of the linked videos are part of a series or channel. That is, there are similar videos on related topics. If you are interested, look for the Subscribe button. Then from the YouTube home page, you can select your Subscriptions.
Table Footnotes
- * I have no idea how they managed to conflate Apple Music and iCloud as the same thing.
- # Yahoo Stocks, or Yahoo! Finance, was a surprise to me. I never would have guessed.
- @ They count The Weather Channel and its widget separately. WTF? The links are about widgets.







